In recent years, the field of robotics has made significant advancements, and robots are increasingly becoming integrated into our daily lives. From the automated vacuum cleaner that tidies our floors to humanoid robots working alongside humans in factories, the interaction between humans and robots is no longer confined to science fiction. This burgeoning field has given rise to the study of the psychology of human-robot interaction (HRI). Understanding how humans perceive, react to, and interact with robots is crucial for designing machines that can coexist harmoniously with us.
The Human-Robot Connection
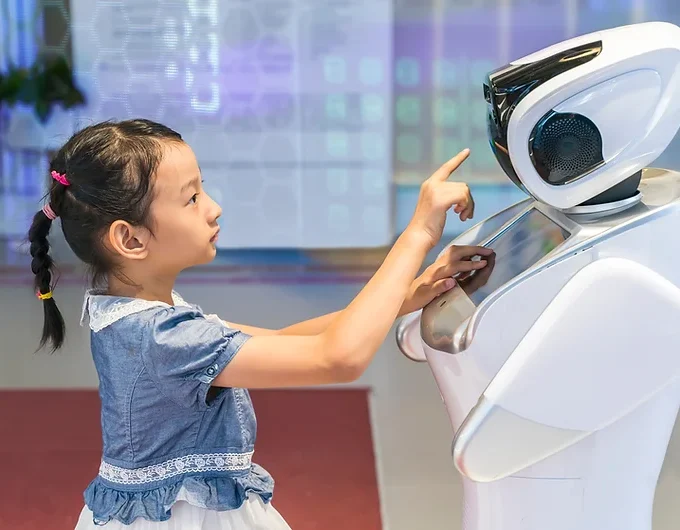
Human beings are social creatures by nature. We are wired to interact with one another, form emotional bonds, and communicate through various modalities. This inherent social nature extends to our interactions with robots. Studies have shown that people tend to anthropomorphize robots, attributing human-like qualities and intentions to them. This tendency to humanize robots forms the basis of the emotional connection that can develop between humans and machines.
One of the reasons behind this anthropomorphism is our inclination to look for familiar cues in the world around us. Robots designed with human-like features, such as a face with expressive eyes or a voice that emulates human speech, trigger our innate social responses. This creates a sense of familiarity and comfort in our interactions with robots, even when we know they lack consciousness or emotions.
Emotions in HRI
Emotions play a significant role in human-robot interactions. Researchers have delved into the realm of affective computing, which aims to make robots more emotionally intelligent by recognizing and responding to human emotions. This is critical for tasks like caregiving robots, where understanding a person’s emotional state is vital for providing appropriate care.
In HRI, humans can experience a range of emotions when interacting with robots. These emotions can be positive, such as trust, empathy, and companionship, or negative, like fear, mistrust, and discomfort. For instance, studies have shown that individuals can form emotional bonds with social robots, even though they are aware that these machines lack genuine feelings. This highlights the remarkable capacity of humans to adapt their emotional responses to suit the context.
Trust and Ethical Considerations
Trust is a fundamental component of any human-robot interaction. In fields like healthcare and autonomous vehicles, trust in the capabilities and decisions of robots is paramount. Trust can be influenced by factors such as robot performance, transparency in decision-making, and the reliability of the technology.
Ethical considerations also play a pivotal role in HRI. Questions about robot rights, privacy, and the potential for robots to reinforce biases or discriminatory behaviours require careful examination. As robots become more integrated into our lives, it becomes essential to establish ethical guidelines and laws to govern their use.
Challenges in HRI
Despite the rapid progress in robotics, there are numerous challenges in the field of HRI. Uncertainty and unpredictability in human behaviour, cultural differences, and the need for robots to adapt to dynamic social contexts are just a few of the complex issues that researchers are tackling.
Additionally, there is a concern that excessive reliance on robots in caregiving or social contexts could lead to social isolation and a decline in human-human interactions. Striking the right balance between robot assistance and human companionship is an ongoing challenge.
The psychology of human-robot interaction is a multifaceted field that delves into the intricacies of how humans perceive, connect with, and trust robots. As robots continue to become integrated into various aspects of our lives, understanding the human side of HRI is vital for designing robots that can seamlessly coexist with us.
By addressing the psychological aspects of HRI, researchers and engineers can create robots that not only perform tasks efficiently but also enhance our overall well-being and quality of life in an increasingly automated world.













Leave a comment